Night driving presents unique challenges that catch many drivers off guard. The National Safety Council reports that fatal car crashes are three times more likely to occur at night, despite significantly less traffic on the roads.
At floridadetscourse.com, we’ve compiled essential night driving safety tips to help you navigate dark roads with confidence. These proven strategies will transform your nighttime driving experience from stressful to secure.
What Vehicle Preparations Matter Most for Night Driving
Your vehicle’s lighting system becomes your lifeline after dark, and proper maintenance is crucial for safe nighttime travel. Start with a thorough headlight inspection and check for cloudy lenses, cracks, or moisture buildup that compromises beam effectiveness. Clean both headlights and taillights with automotive glass cleaner and a microfiber cloth, and pay special attention to road grime and salt residue that accumulates during winter months. Misaligned headlights create dangerous blind spots, so verify that your low beams illuminate the road 25 feet ahead and high beams reach 100 feet forward without blinding oncoming drivers.
Windshield and Glass Maintenance
Your windshield requires meticulous attention before nighttime drives, as even minor streaks multiply glare from oncoming headlights. Use ammonia-based cleaners on both interior and exterior surfaces and wipe in circular motions to eliminate streaks. Replace windshield wipers every six months, as worn blades leave water streaks that scatter light and reduce visibility. Check for chips or cracks larger than a quarter, which can spread under temperature changes and create dangerous distortions in your field of vision.
Complete Light System Check
Test every light on your vehicle systematically and start with headlights on both low and high beam settings. Walk around your car to verify that brake lights, turn signals, hazard lights, and reverse lights function properly. Dashboard illumination should be adjustable to prevent eye strain while it maintains gauge visibility. Replace any burned-out bulbs immediately, as failed lighting systems create safety hazards for nighttime driving. Interior dome lights should work reliably for emergency roadside situations, but keep them dimmed while you drive to maintain night vision adaptation.
Mirror and Window Adjustments
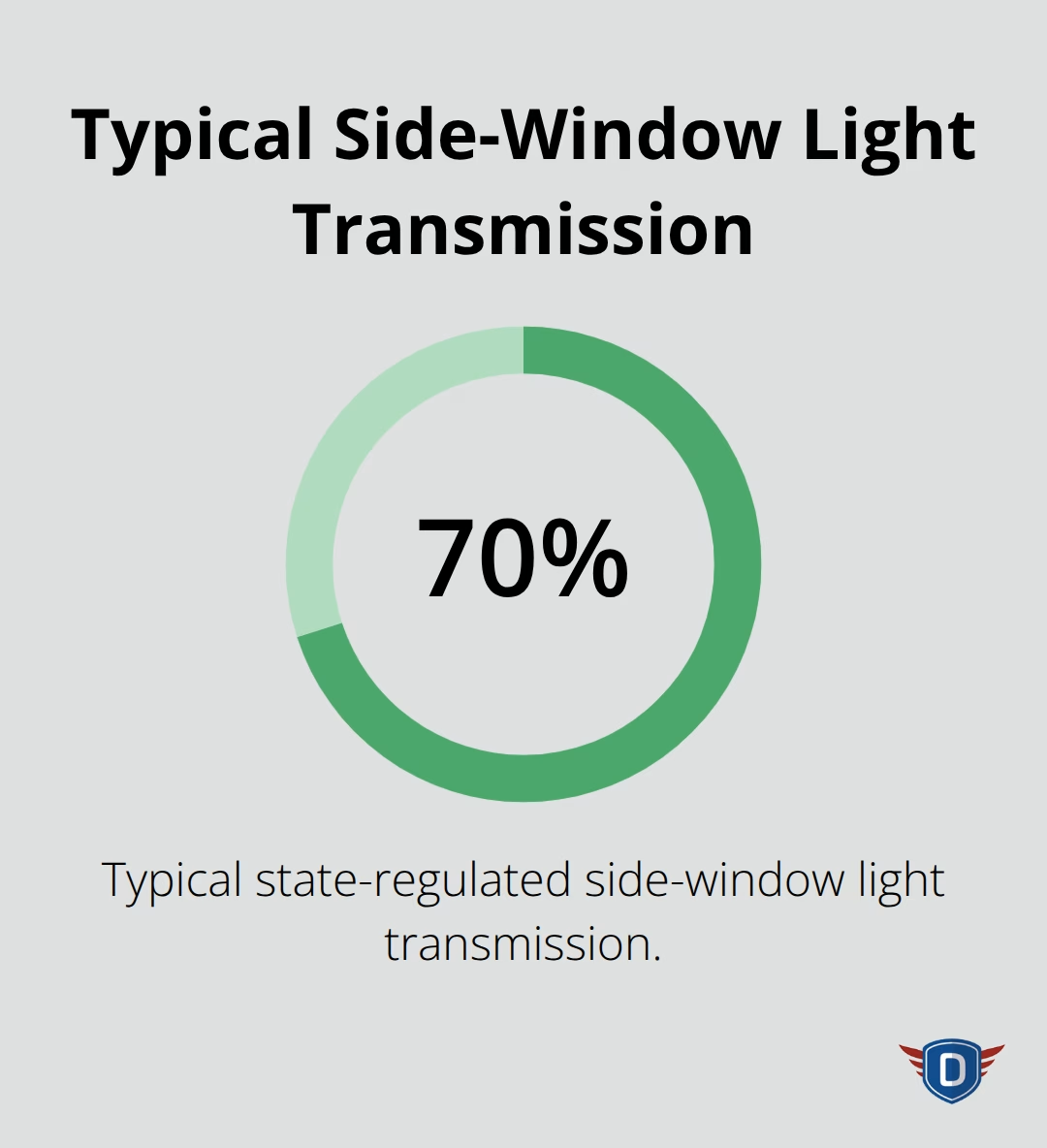
Position your rearview and side mirrors to minimize blind spots before you start your night drive. Clean all mirrors thoroughly to remove fingerprints and dust that scatter light from following vehicles. Adjust your seat height so you can see over the steering wheel comfortably while you maintain a clear view of the road ahead. Tint levels on side windows should comply with state regulations (typically 70% light transmission) to avoid further visibility reduction at night.
These vehicle preparations set the foundation for safe nighttime travel, but proper technique becomes equally important once you’re behind the wheel. Remember that driving in adverse conditions requires additional preparation and awareness beyond standard night driving protocols.
How Do You Master Night Driving Techniques
Headlight management separates confident night drivers from those who struggle after dark. Switch to high beams on rural roads and highways when no oncoming traffic appears within 500 feet, as the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety recommends. High beams illuminate up to 450 feet ahead compared to just 160 feet with low beams, which gives you extra reaction time. Dim your high beams immediately when you spot vehicles ahead or when you follow another car closer than 200 feet.

Strategic Distance Management
Double your normal distance during night drives to compensate for reduced visibility and slower reaction times. Research from the Federal Highway Administration’s Visibility Research Program shows that night driving presents significant safety challenges due to reduced visibility conditions. Use the four-second rule instead of the standard three-second rule and count the time between when the vehicle ahead passes a fixed object and when you reach the same point. This extended buffer becomes essential when your headlights only illuminate 160 feet ahead at 40 mph, while you need 190 feet to stop completely.
Advanced Visibility Techniques
Focus your eyes on the right edge of the road rather than stare directly into oncoming headlights to avoid temporary blindness from glare. Shift your gaze continuously between the road ahead, your mirrors, and the dashboard to maintain situational awareness without fixation on any single point. Night driving requires enhanced visual strategies, particularly for older drivers who may experience greater difficulty with reduced lighting conditions. Keep your dashboard lights dimmed to prevent interference with your night vision adaptation, which takes up to 30 minutes to fully develop after you leave bright environments.
Speed Adjustment Strategies
Reduce your speed by 10-15 mph below daytime limits to account for limited visibility and increased reaction times. The National Safety Council emphasizes that slower speeds provide more time to identify and respond to hazards that appear suddenly in your headlight beams. Wildlife becomes particularly active between dusk and dawn, with deer collisions peaking from October through January. Lower speeds also help you maintain better control when you encounter unexpected obstacles or road conditions that become visible only at the last moment.
These techniques form the foundation of safe night travel, but specific hazards require targeted strategies to navigate successfully.
What Night Hazards Threaten Your Safety Most
Oncoming headlight glare creates temporary blindness that causes accidents annually, yet most drivers handle this hazard incorrectly. Research shows that headlight glare was cited as a factor in only one or two out of every thousand nighttime crashes across 11 U.S. states from 2015 to 2023. Focus your eyes on the white line or right edge of the road when you approach bright headlights, and slow down immediately to compensate for reduced visibility. Adjust your rearview mirror to the night position to deflect glare from vehicles behind you, and clean your windshield thoroughly since dirt amplifies scattered light by up to 50 percent.
Wildlife Collision Prevention
Animal strikes peak between October and January when deer movement increases, with most collisions between 6 PM and midnight according to State Farm data. Deer travel in groups and freeze when startled by headlights, so never swerve if you spot one animal since others likely follow nearby. The Insurance Institute for Highway Safety found that animal collisions caused 235 deaths in 2023, with deaths from these collisions increasing from 89 in 1975 to 223 in 2007. Scan road edges continuously in rural areas and reduce speed in zones marked with wildlife crossings (these signs indicate high-risk areas). Honk your horn in short bursts if you see animals near the roadway, as this often motivates them to move away from traffic.
Drowsy Driver Recognition
Microsleeps last 4-5 seconds and occur without warning when fatigue sets in, during which your vehicle travels the length of a football field at 55 mph. The National Sleep Foundation reports that 37 percent of drivers have fallen asleep while behind the wheel, with crashes most likely between midnight and 6 AM. Watch for these warning signs: frequent yawns, heavy eyelids, drift between lanes, missed exits, or inability to recall the last few miles driven. Pull over immediately at the first rest area when you experience any drowsiness symptoms, as caffeine takes 30 minutes to become effective and provides only temporary alertness.

Final Thoughts
Night driving safety tips become second nature through consistent practice and proper preparation. The statistics speak clearly: fatal crashes triple after dark, which makes these techniques essential rather than optional for every driver. Regular practice builds confidence and muscle memory for headlight management, distance control, and hazard recognition.
Schedule monthly night drives on familiar routes to reinforce proper techniques before you tackle unfamiliar roads in darkness. Your skills deteriorate without practice, particularly the visual patterns that prevent accidents. Professional instruction accelerates your progress significantly and helps you master advanced techniques through personalized guidance.
Vehicle maintenance remains equally important as technique. Monthly headlight checks, windshield inspections, and system tests prevent equipment failures that cause accidents (replace worn components immediately rather than risk nighttime emergencies). We at floridadetscourse.com offer comprehensive driver education programs that help transform nervous night drivers into skilled, confident operators who navigate dark roads safely.